Copper Toxicosis (Copper Storage Hepatopathy)
For Labrador Retrievers, Labradoodles, and Doberman Pinschers
Order Dog DNA Tests by Breed
In our state-of-the-art laboratory, we perform dozens of validated DNA tests for hundreds of breeds: Type in your dog’s breed and hit "Search" to see the possibilities. For dogs of unknown descent, type “mixed breed."
Breeder Concierge Service
If you need assistance ordering, you're welcome to call us directly at 800.625.0874 or email our team using the form on this page. We'll get back to you as soon as possible to help you place your order!
TO PLACE INTERNATIONAL ORDERS PLEASE CALL 513-881-7806 @ Ext. 5826

Test Highlights:
Name: Copper Toxicosis
DNA Samples: Collected at Home Using Cheek Swabs
Cost: $58 + S&H per Dog/Multi-Test Discounts may Apply
Results: 5 Business Days after Receipt of Samples
For Labrador Retrievers, Labradoodles, and Doberman Pinschers
Copper Toxicosis (CT) is an inherited autosomal recessive disorder in which a dog’s system accumulates excess copper instead of excreting it naturally. CT affects several dog breeds and can result in severe damage to the liver and—eventually—liver disease, failure, and possibly death.
DDC Veterinary has validated an accurate and reliable genetic CT test for Labrador Retrievers, Labradoodles, and Doberman Pinschers to help breeders avoid producing CT at-risk offspring.
Our DNA assay for this inherited form of Copper Toxicosis detects the mutations in these two genes:
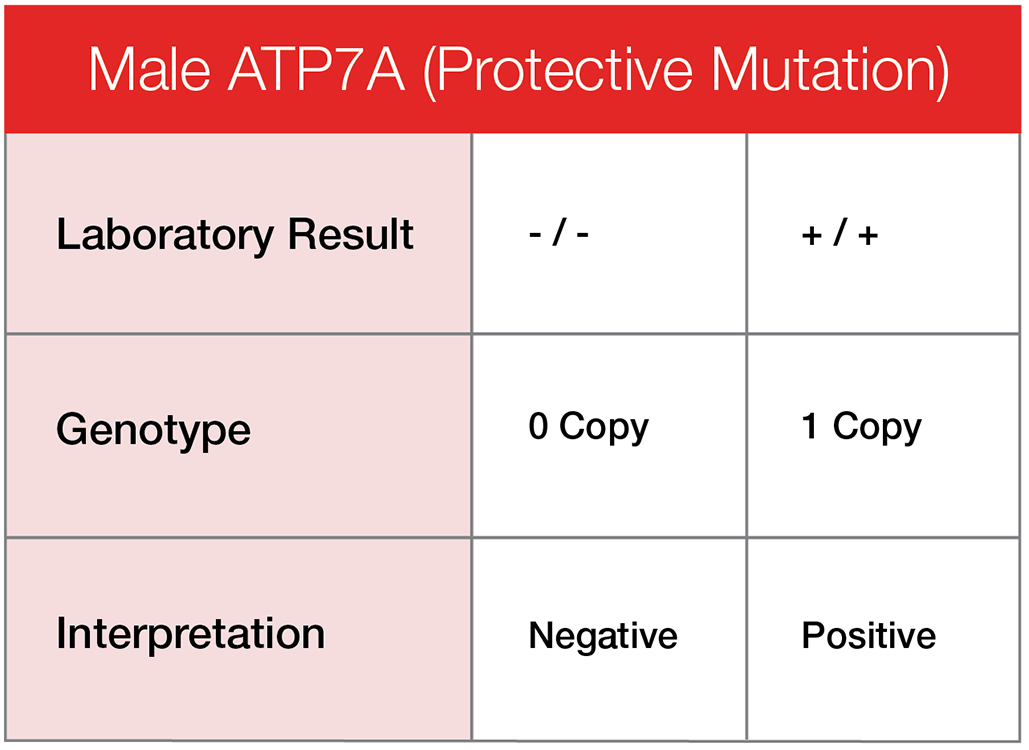
ATP7A: a modifier mutation that can reduce the effects of the disease mutation. Females may have two copies (affected), one copy (carrier) or no copies (clear). Males may have one copy (affected) or no copies (clear).
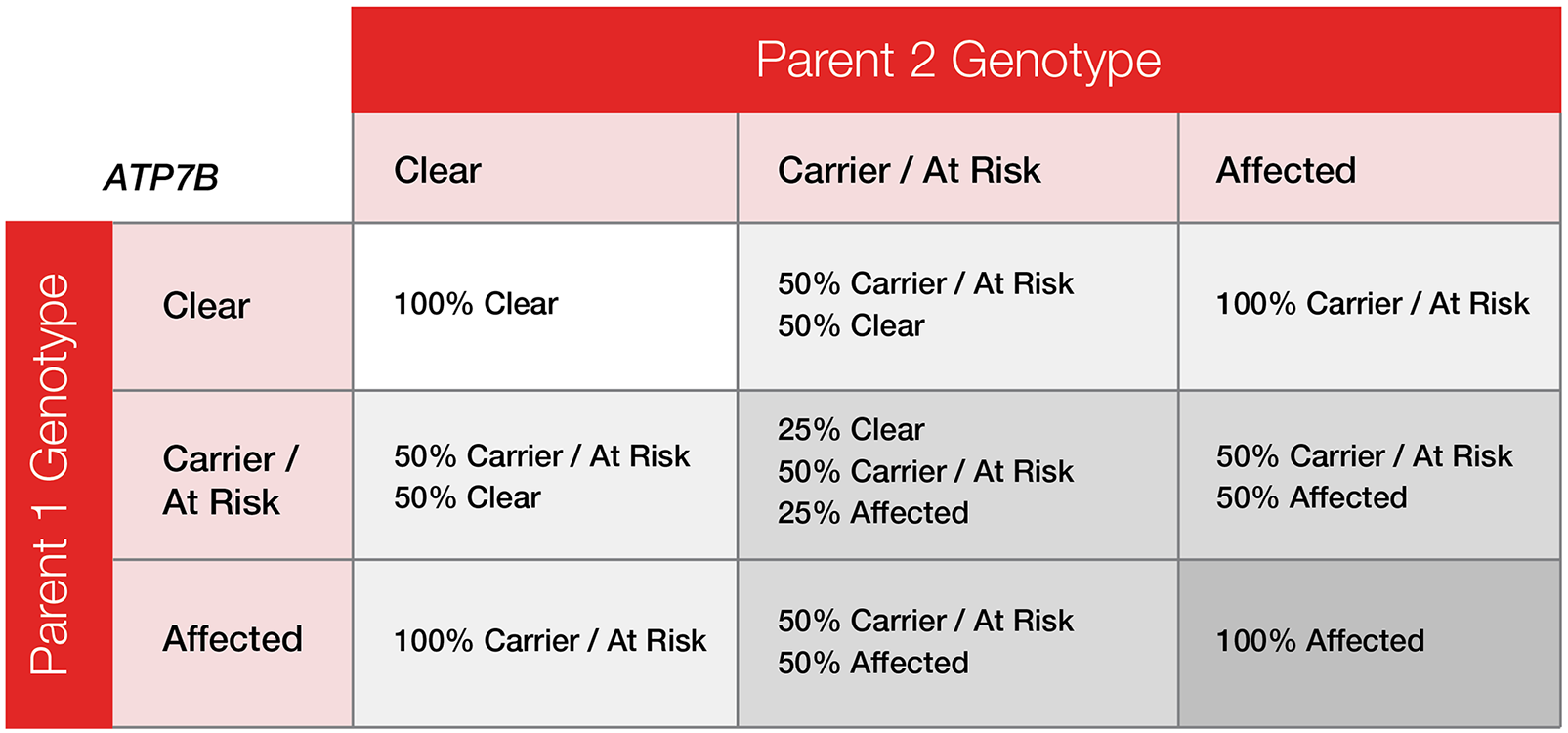
ATP7B: the disease mutation. Dogs with two copies or one copy of this mutation are both considered to be at risk for developing the disease.
The DNA test for disease mutation ATP7B reveals one of 3 possible genotypes:
- CLEAR (those having 2 copies of the normal allele and appear to be normal)
- CARRIER/AT RISK (those having 1 copy of the normal allele and 1 copy of the disease mutation = 1+ At Risk for clinical signs)
- AFFECTED (those having 2 copies of the disease mutation = 2+ At Risk for clinical signs)
The protective mutation ATP7A works to provide some form of risk reduction from the disease mutation, when present. The number of possible copies is dictated by gender. Only the X chromosome can carry a copy of the ATP7A, which is why males cannot carry two copies (they are XY). The Y chromosome will not carry a copy of the protective mutation.
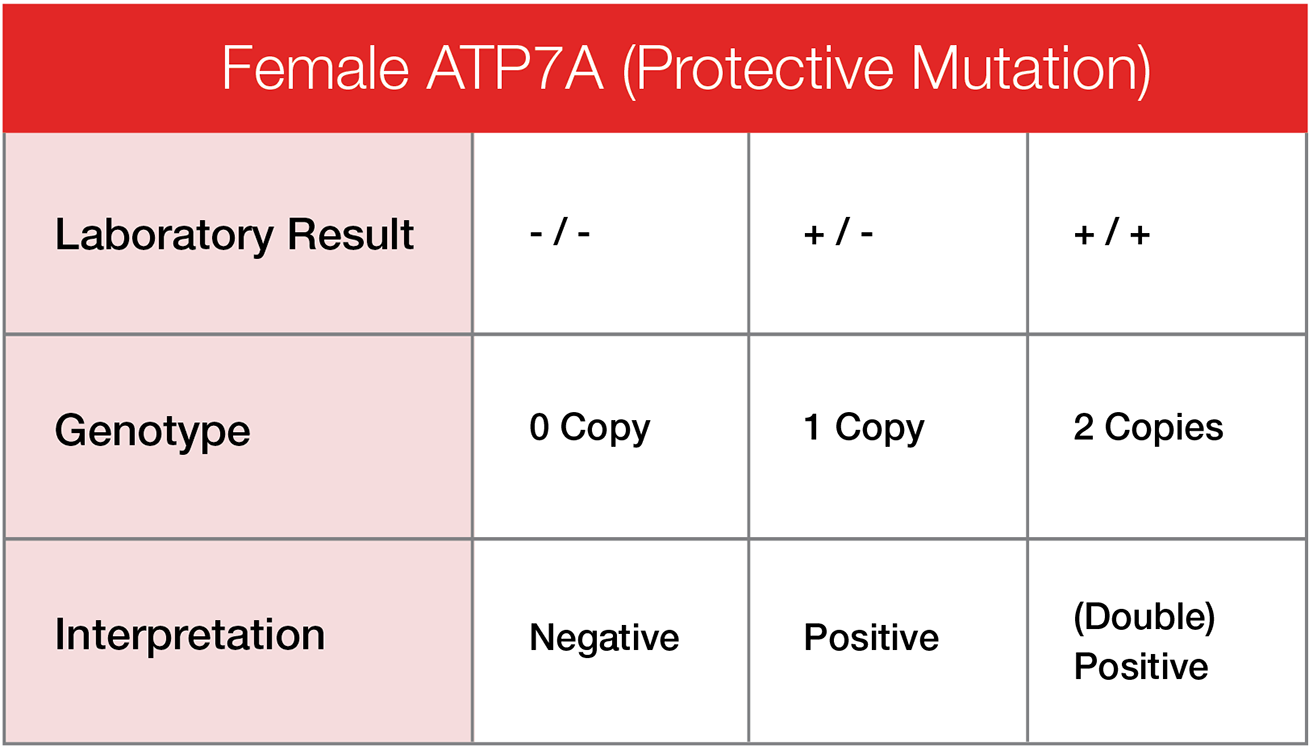
The effects of the disease mutation may be reduced based on the dog’s genotype for the protective mutation.
These mutations are most associated with CT in Labrador Retrievers and Labradoodles; they have also been found in Doberman Pinschers and have been associated with CT in this breed. Presence of these mutations in other unrelated breeds has not been currently documented.
IMPORTANT: This test does not detect the COMDD1 mutation causing a similar disorder in Bedlington Terriers.
Next Steps after Testing
Because there are other factors that may contribute to the exhibition of symptoms of CT, it is important to share test results with your veterinarian. Should your animal test positive for the disease marker it may be necessary to regularly monitor copper levels in the dog, regardless of whether or not your dog has the ATP7A protective mutation.
Reach Us
Have questions or need assistance? Contact our team.
DNA Technology Park
1 DDC Way
Fairfield, OH 45014
USA: 1.800.625.0874
INT: 1.513.881.7800